Reforming Florida’s direct file system will improve public safety outcomes and help sustainably balance the budget, according to a new policy brief entitled “No Place for A Child.” Prosecutors in Florida transfer more youth to the adult criminal justice system, without any checks or balances, than in any other state in the country.
The new research came out the same morning the Florida senate moved forward on direct file reform legislation. On Thursday, Senate Bill 314 earned a second unanimous vote of support from the Florida Senate Appropriations Subcommittee on Criminal and Civil Justice. The Republican subcommittee chairman thanked the researchers for their work after hearing from Floridian judges and advocates who support the bill.
The authors of the brief, researchers from the free market–oriented James Madison Institute and the Florida State University Project on Accountable Justice, gathered FY2010 data from the Florida Department of Juvenile Justice (DJJ) and Department of Corrections (DOC) to provide unique insights into the fiscal and social impact of reining in direct file. Their research complements a recent website with specific stories of direct-file Florida youth.
Direct file – a unilateral transfer performed by prosecutors before any hearing or due process can occur – accounts for 98% of the state’s cases of minors in the adult system, which remarkably totaled more than 10,000 cases in the past five years. Ending or reforming the practice of direct file would allow youths’ cases to be more fairly considered by a judge for transfer, and would greatly reduce the total number of transferred youth in the state.
This decrease of youth in the adult system would move more children back to a system that focuses on rehabilitation, which is especially appropriate because both DOC and DJJ data suggest that direct-filed youth would pose a low risk in the juvenile justice system. In fact, the researchers use government risk assessment tools and find that if direct-filed youth were processed in the juvenile justice system, fully 87% would not be placed in secure detention.
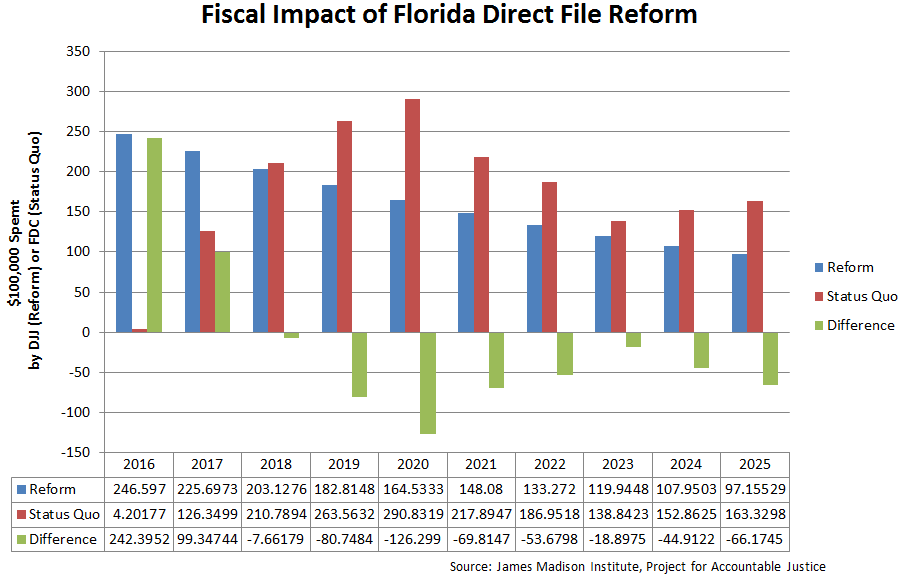
Moreover, the policy brief finds that keeping direct file–eligible youth in the age-appropriate juvenile justice system would save the state $12.6 million in ten years, with annual savings accumulating annually just four years after the reform. The authors point out that placing youth in the adult system demonstrably harms rehabilitation; in their words, “the adult system sets children up to fail.” Nonetheless, another decade of the status quo would cost Floridian taxpayers more than $175 million dollars.
Similar to adults’ cases, almost all of children’s cases in Florida’s adult system end in plea bargains, the brief finds. When a plea deal or a sentencing decision leads to probation for youth, which occurred in 72% of children’s cases in FY2010, 53% of youth on probation ended up in prison, either for a felony (70%), or for a probation violation (30%).
Without access to the rehabilitative services offered by the juvenile system, the authors note, youth have no developmentally-appropriate guidance to reform their behavior. Poor outcomes with adult-system probation reflects near-certain causative evidence that placing children in the adult system significantly raises transferred youths’ recidivism rates.
The researchers call for reform of direct file after concluding that the practice negatively affects public safety, children’s mental health and potential to reform, and the state’s budget. Finding a way to offer more due process and rehabilitative opportunities for children, they say, will be “unambiguously positive” for the state, its government, and its young adults.
A direct link to the research is available here.
You can read more about the lives affected by direct file practices in Florida by visiting www.noplaceforachild.com.